Congenital Heart Defects - Types - Types
There are many types of congenital heart defects. They range from simple to complex and critical. Simple defects, such as atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defects, may have no symptoms and may not require surgery. Complex or critical defects such as hypoplastic left heart syndrome may have severe, life-threatening symptoms. Babies born with a critical congenital heart defect typically have low levels of oxygen soon after birth and need surgery within the first year of life.
Atrial septal defect
-
Congenital Heart Defects - Types
An atrial septal defect is a hole in the wall between the atria, which are the two upper chambers of the heart. The hole causes blood to flow from the left atrium and mix with the right atrium, instead of going to the rest of the body. Atrial septal defect is considerered a simple congenital heart defect because the hole may close on its own as the heart grows during childhood, and repair may not be necessary.

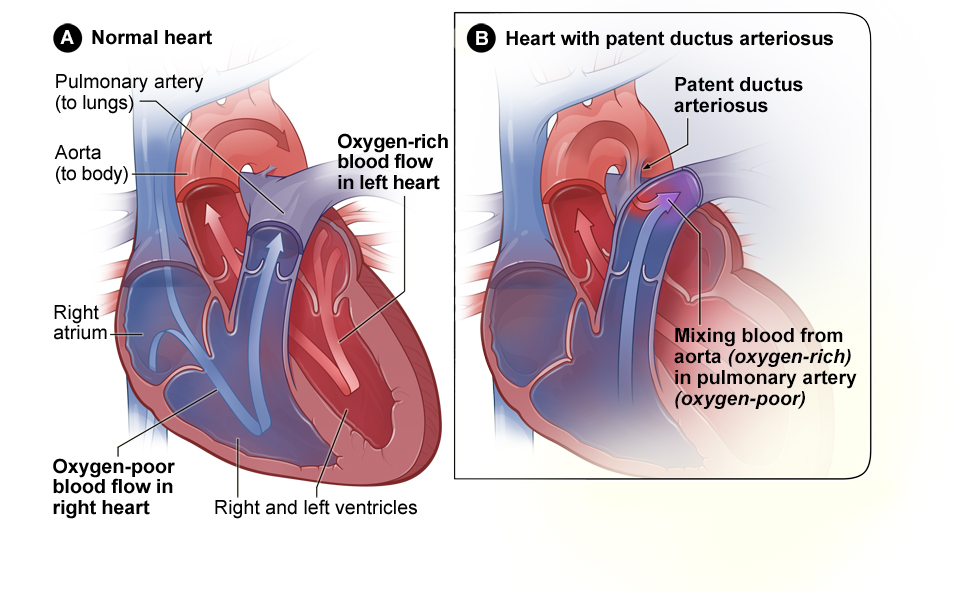
Patent ductus arteriosus
-
Congenital Heart Defects - Types
This common type of simple congenital heart defect occurs when a connection between the heart’s two major arteries does not close properly after birth. This leaves an opening through which blood can flow when it should not. Small openings may close on their own.
Pulmonary stenosis
-
Congenital Heart Defects - Types
Pulmonary stenosis is a narrowing of the valve through which blood leaves the heart on its way to the lungs. Visit our Heart Valve Disease Health Topic to learn more. Many children with pulmonary stenosis do not need treatment.
Ventricular septal defect
-
Congenital Heart Defects - Types
A ventricular septal defect is a hole in the wall between the ventricles , which are the two lower chambers of the heart. Blood may flow from the left ventricle and mix with blood in the right ventricle, instead of going to the rest of the body. If the hole is large, this may make the heart and lungs work harder and may cause fluid to build up in the lungs.

Tetralogy of Fallot
-
Congenital Heart Defects - Types
This is the most common complex congenital heart defect. Tetralogy of Fallot is a combination of four defects:
- Pulmonary stenosis.
- A large ventricular septal defect.
- An overriding aorta. With this defect, the aorta is located between the left and right ventricles, directly over the ventricular septal defect. As a result, oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle can flow directly into the aorta instead of into the pulmonary artery.
- Right ventricular hypertrophy. In this case, the muscle of the right ventricle is thicker than usual because it has to work harder than normal.

Other critical congenital heart defects
-
Congenital Heart Defects - Types
Common congenital heart defects include:
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Double-outlet right ventricle
- D-transposition of the great arteries
- Ebstein’s anomaly
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- Interrupted aortic arch
- Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
- Single ventricle
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
- Tricuspid atresia
- Truncus arteriosus

